Somewhere in life, I'd guess ten percent of the general public will develop warts. Two skin afflictions that plague any individual are common warts and toenail fungus but are characteristically distinct in terms of etiology and therapy. Warts, small epidermal bumps on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), differ from toenail fungus, or onychomycosis, fungal infection in toenails. Let's go through warts types mixed with toenail fungus, poll in our heads, and press information into practice for therapy and identification.
Types of Wart
Common Warts (Verruca Vulgaris)
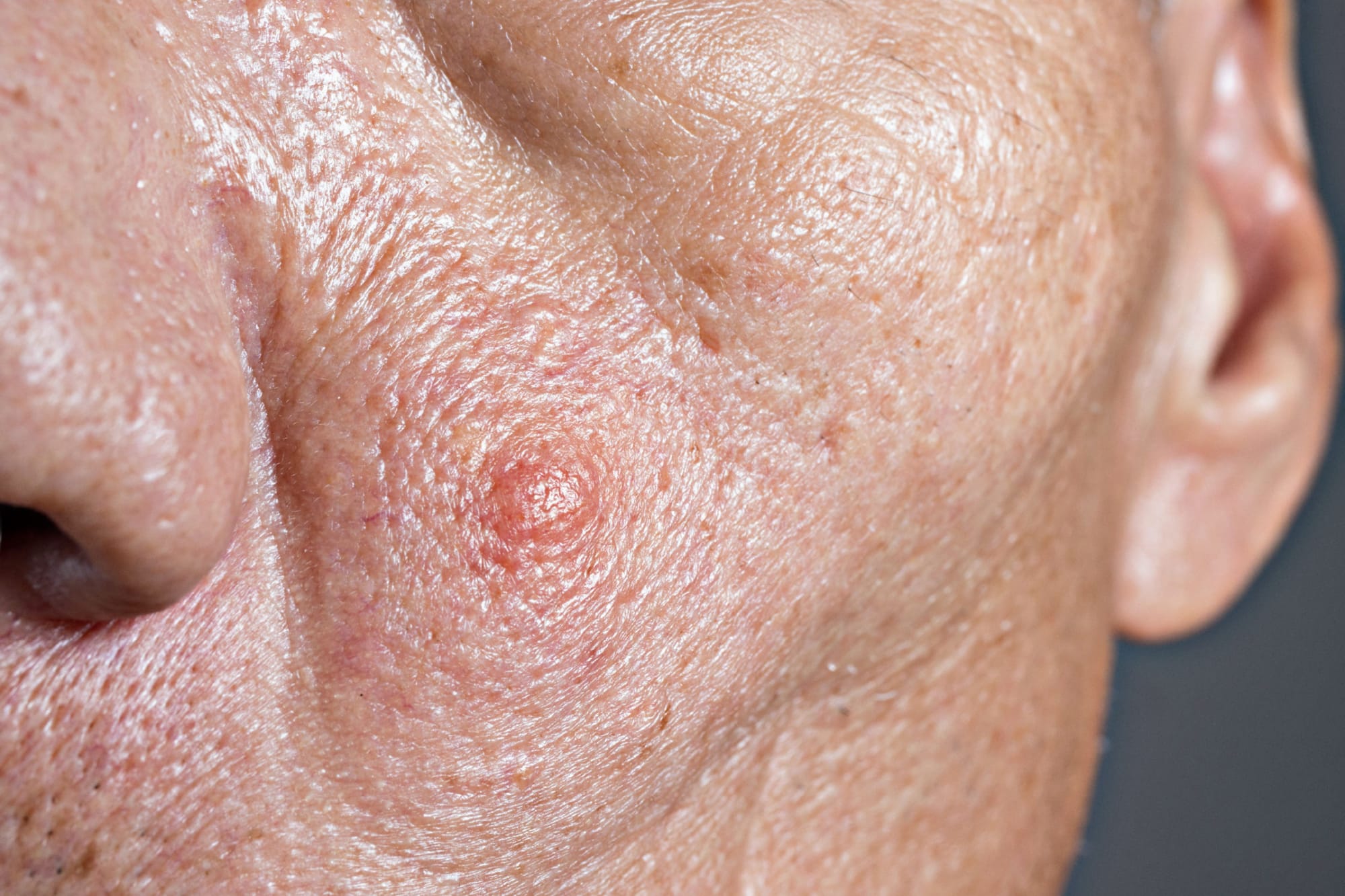
Minute rounded rough-granular eruptions with a rough, grainy top and rough, grainy textured top and exterior with a tendency to appear between fingers, hands, and surrounding fingers and toenails, common warts have a normal-thought possibly a grizzled and tawny hue. One in ten humans and 7% of society at one time suffers from common warts.
Plantar Warts
Plantar warts most often develop in the base of the foot and produce hindered and painful walking. An unlucky position, that brings to mind a recall of the shape of calluses, with miniature black specks (thrombosed blood vessels) present. Imagine a teenager's horror: agonisingly practicing in amongst his mates with plantar warts.
Flat Warts (Plane Warts)
Flat warts occur in level heads, which under normal circumstances, are not grainy, smaller, and flesh-colored to tan in color. Most frequently, they occur in groups, recurring in clusters, on the face, forearms, and shins. Unlike ordinary warts, flat warts are less elevated in height, again with a similar but darker coloration.
Genital Warts (Anogenital Warts)
Genital warts result from HPV (43 of them cause infection in the genitalia). Some of them cause low-risk warts in the genitalia, and a subset of high-risk ones cause degenerating cancers. Approximately 1 out of 4 sexually active adults in America have an HPV infection, estimates say.
TOENAIL FUNGUS
Symptoms and Appearance:
Toenail fungus can become apparent in a discoloration in white or yellowish at the tip of a toenail. It can extend under the toenail, therefore putting a victim at risk for thickening, discoloration, and crumbling at the edge. As a consequence, an estimate is that approximately 10% of the population could be involved, and with age, susceptibility could increase.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Toenail fungus comfortably lives in warm and moist environments, poor foot hygiene, age, and diabetes mellitus, and a range of factors, are other factors involved. As a consequence, washing and drying out of the feet is one of the most significant actions one can make when one seeks to avoid a toenail infection of a fungal origin.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
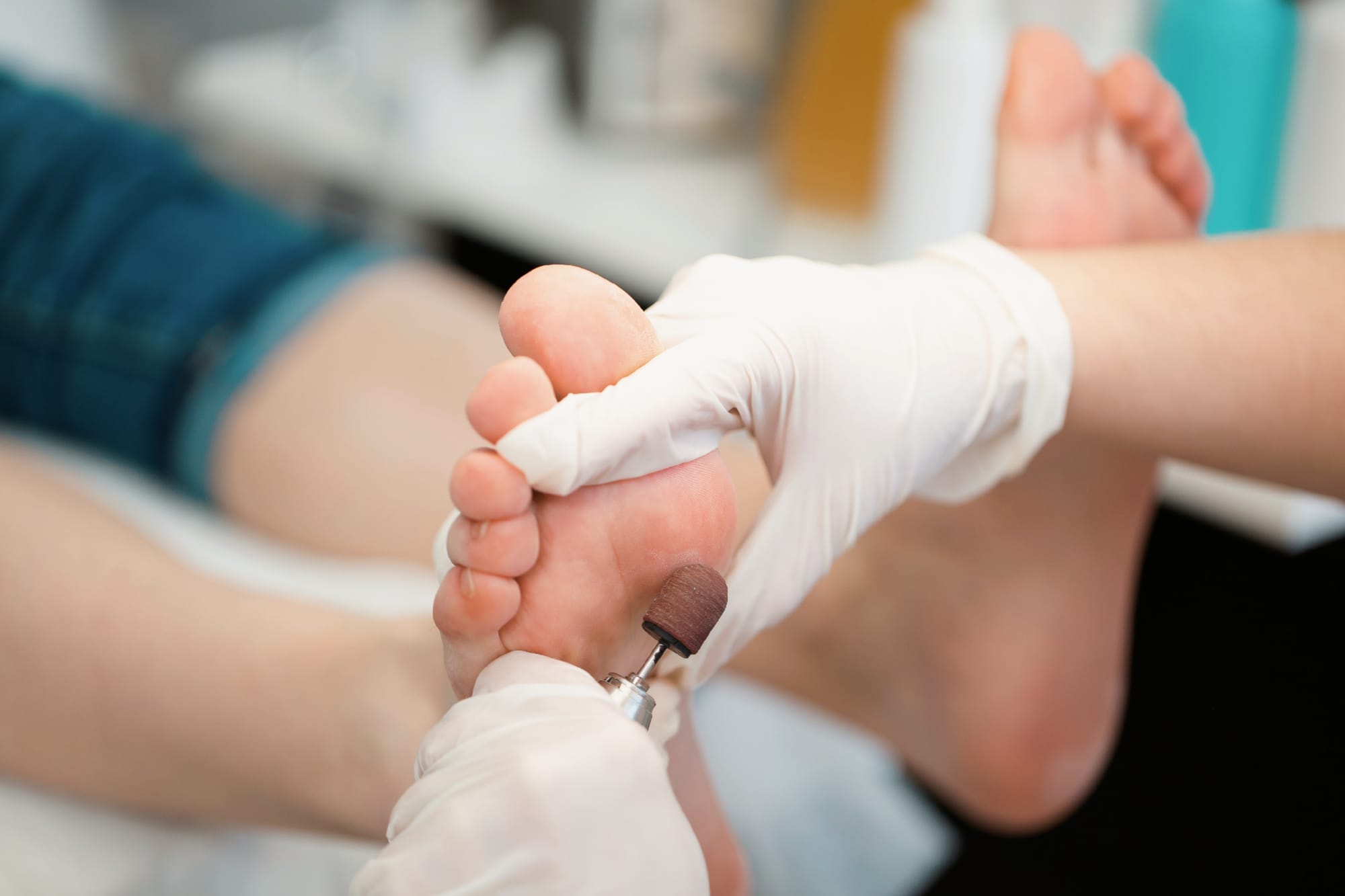
Toenail fungus involves examination of a nail, with a little collection for certain laboratory tests in a few cases. Topical, systemic, and laser therapy are part of common drugs involved. In an attempt to avert a repeat, clip off the nails regularly and don't go bare in public places.
Warts appear most often in hands, in elbows, and in knees, and toenail fungus in toenail areas. Feeling for epidemiology can guide preliminary evaluation. For instance, warts in hands appear very frequently in kids, and toenail fungus infection is relatively common in adults.
Differentiating Warts and Toenail Fungus
Visual Differences
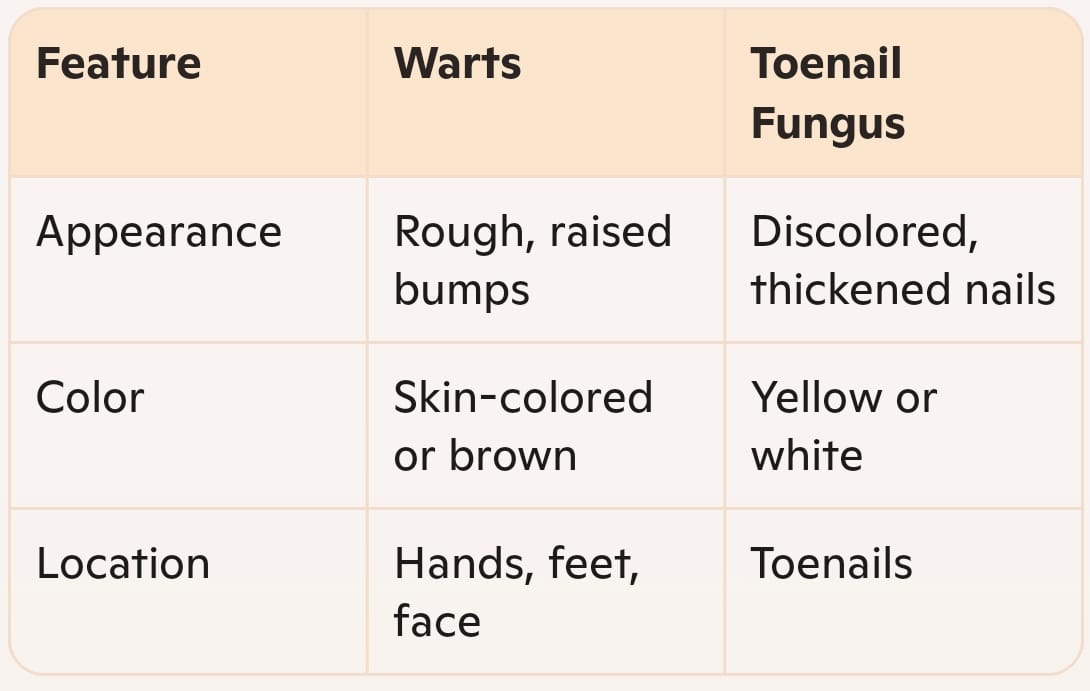
Location Differences
Warts usually appear on hands, elbows, and knees, while toenail fungus is limited to toenails. Knowing where each condition typically occurs can aid in initial assessments. For instance, warts on the hands are common in kids, while toenail fungus often develops in adults
Treatment Variations
While warts can be treated in general with topical therapy, cryotherapy, and with surgery, toenail fungus can be taken care of with antifungals and sometimes even with drugs in mouth. In view of individual requirements, severity, and suitability of a specific remedy for a patient in a case, there is a remedy scheme. Consultation with some medical expert will maximize positive results. Warts appear most in hands, in elbows, and in knees, and toenail fungus in toenail areas. Feeling for epidemiology can guide a preliminary evaluation. For instance, warts in hands appear very frequently in kids, and toenail fungus infection is relatively common in adults. While warts can be treated in general with topical therapy, cryotherapy, and with surgery, toenail fungus can be taken care of with antifungals and sometimes even with drugs in mouth. In view of individual requirements, severity, and suitability of a specific remedy for a patient in a case, there is a remedy scheme. Consultation with some medical expert will maximize positive results.
When Shall I Seek Professional Help?
Signs that could indicate a need for professional assistance include warts that spread quickly or in case of fungal infection, the presence of accute pain. The prognosis markedly improves with early intervention. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is critical to consult a podiatrist or dermatologist.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Caring for chronic problems must be ongoing. This involves good hygiene, regular check-ups, and using antifungal powder in shoes. Knowledge of these conditions helps in working on preserving long-term health.
Conclusion

Understanding the differences between warts and toenail fungus is vital to treatment. Each variant of wart has a defining characteristic, and toenail fungus can pose distinct challenges. It is necessary to resort to the clinic or hospital for diagnosis and treatment planning based on the needs of each patient. Given prompt action in both cases, OTC products can provide treatment and prevention benefits. Addressing these concerns among skin and nail problems with proper interventions is just the right measure to keeping healthy skin and nails, a gainful endeavor for better quality of life.


