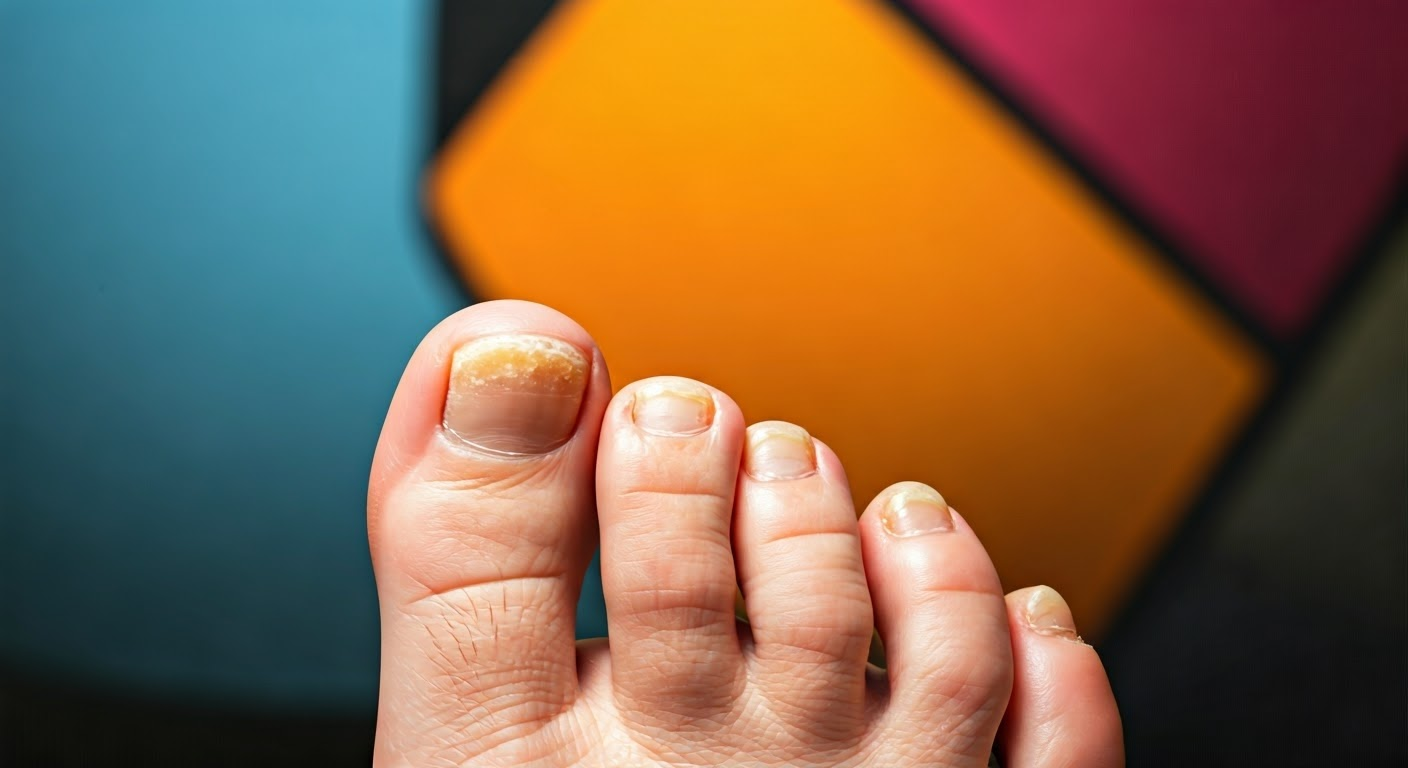
Toenail fungus, or onychomycosis, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Although it is often benign in its early stages, the symptoms can sometimes be confused with other nail disorders. This comprehensive guide aims to help you recognize the signs of toenail fungus, distinguish it from similar conditions, and explore various treatment options available.
What is Toenail Fungus?
Toenail fungus is a fungal infection that primarily targets the toenails but can also affect fingernails. It typically arises when fungi enter through cracks or breaks in the nail or surrounding skin. This condition can lead to a range of unpleasant symptoms, including discoloration, thickening, and deformation of the nail. While it may not be painful initially, it can become uncomfortable or even painful if left untreated.
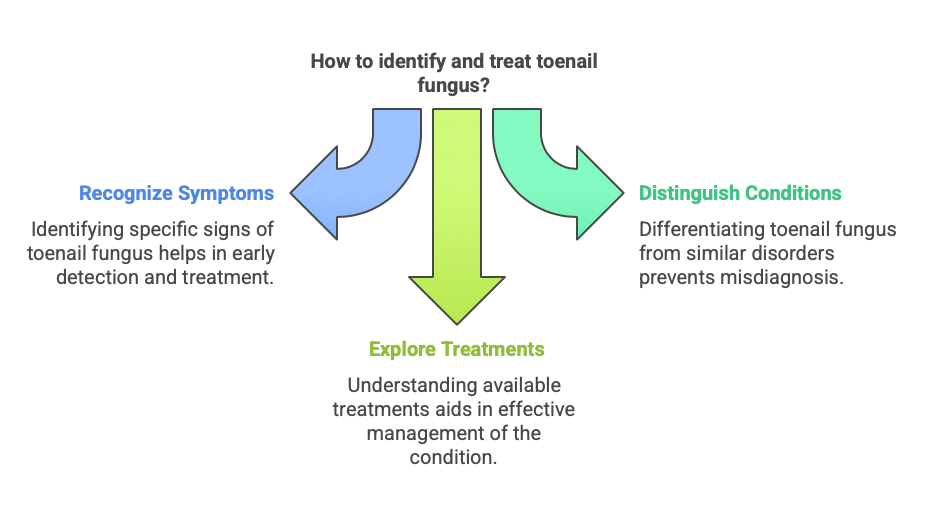
Signs of Toenail Fungus
Identifying toenail fungus early can make treatment more effective. Here are some common signs to look out for:
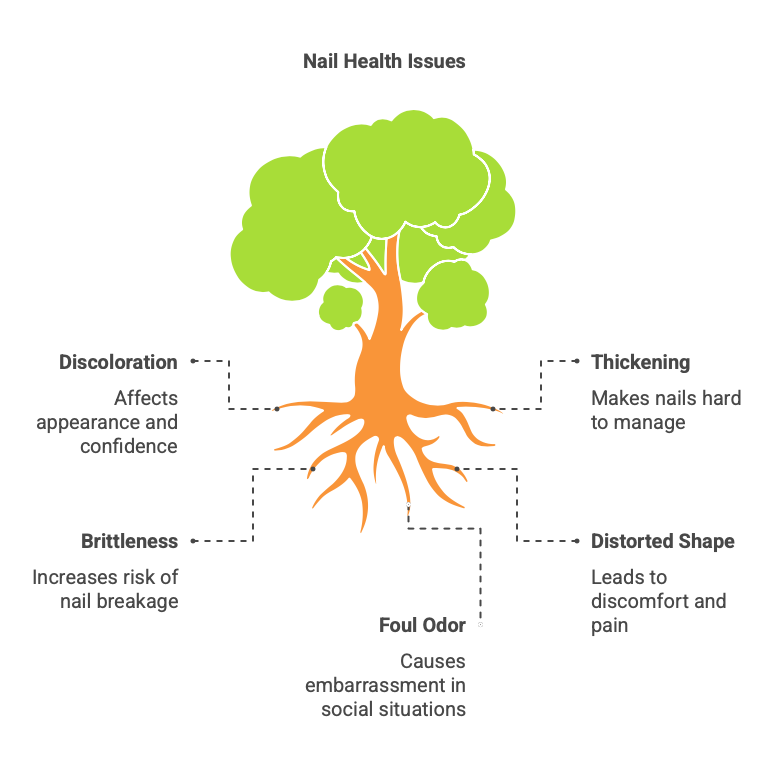
1. Discoloration: The affected nail may appear yellow, brown, or white. In some cases, you might notice dark spots or streaks.
2. Thickening: The nail may become noticeably thicker than usual, making it difficult to trim or manage.
3. Brittleness: Affected nails often become brittle and may crumble at the edges or break easily.
4. Distorted Shape: The nail can change shape or become irregular, and in severe cases, it may separate from the nail bed.
5. Foul Odor: An unpleasant smell may emanate from under the affected nail, which can be particularly noticeable when shoes are removed.
Differentiating from Other Conditions
Toenail fungus can often be mistaken for other nail issues. Here’s how to differentiate it from similar conditions:
• Psoriasis: This autoimmune condition can affect the nails, leading to pitting, discoloration, and thickening. Unlike fungal infections, psoriasis may also cause changes in skin appearance around the nails.
• Injury: Trauma to the nail (such as stubbing your toe) can cause discoloration and thickening that resembles fungal infections. However, injury-related changes typically develop more rapidly and are associated with pain.
• Bacterial Infection: Bacterial infections can also lead to nail discoloration and swelling but often progress more quickly than fungal infections and may present with redness and warmth around the nail.
Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis of toenail fungus, a healthcare provider may employ several methods:
• Visual Examination: A thorough examination of the affected nails and surrounding skin.
• Scraping for Microscopic Examination: The provider may scrape debris from under the nail to examine it under a microscope for fungal elements.
• Nail Clipping for Fungal Culture: A sample of the nail may be sent to a laboratory to identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
Treatment Options and its Relation to How Severe the Condition is:
1. Topical Medications: For mild cases, antifungal nail polish or creams that are applied directly to the nail may be effective. These include over-the-counter options like clotrimazole or prescription treatments like ciclopirox.
2. Oral Medications: More severe infections may require oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine or itraconazole. These medications work from within the body to eliminate the fungus.
3. Laser Therapy: This newer treatment option uses focused light to target and kill the fungus without damaging surrounding tissue. While promising, laser therapy can be costly and may not be covered by insurance.
4. Nail Removal: In extreme cases where the infection is severe and persistent, surgical removal of the infected nail may be necessary to allow new, healthy nail growth.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing toenail fungus is key to maintaining healthy nails. Consider these strategies:
• Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Regularly wash and thoroughly dry your feet, especially between the toes.
• Wear Breathable Shoes and Socks: Opt for shoes made from materials that allow air circulation. Choose moisture-wicking socks to keep your feet dry.
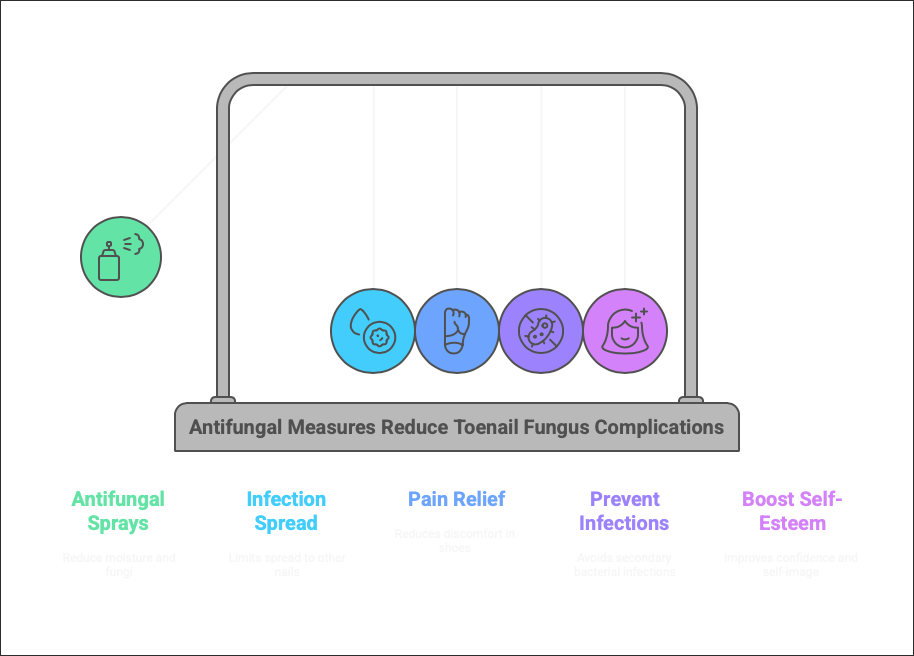
• Use Antifungal Sprays in Shoes: Consider using antifungal powders or sprays inside your shoes to reduce moisture and fungal growth.
• Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Areas: Protect your feet in communal spaces like locker rooms, swimming pools, and showers by wearing flip-flops or water shoes.
Complications of Untreated Toenail Fungus
If left untreated, toenail fungus can lead to several complications:
• Spread to Other Nails or Skin: The infection can easily spread to adjacent nails or even other parts of the body.
• Pain When Wearing Shoes: As the infection progresses, it can cause discomfort or pain when wearing shoes, affecting mobility.
• Secondary Bacterial Infections: The compromised integrity of the nail can lead to bacterial infections that may require additional treatment.
• Negatively Impact Self-Esteem: Visible nail infections can affect an individual’s self-image and confidence, leading to social withdrawal or anxiety.
Conclusion
While toenail fungus is a common issue, obtaining an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare provider is crucial for effective treatment. By recognizing the signs early and understanding your treatment options, you can manage most cases of toenail fungus successfully. Don’t ignore changes in your toenails; early intervention is vital in preventing more serious complications down the road. If you suspect you have toenail fungus or if you’re experiencing any concerning symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance tailored to your situation.